What is Kidney Failure? | Why Does Kidney Failure Occur? |Prevention of Kidney Failure | The Importance of Early Detection.
eshoiorg
- March 5, 2025
What is Kidney Failure?
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure, occurs when the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood effectively. This can lead to a dangerous buildup of toxins and fluids in the body, disrupting essential functions. There are two main types of kidney failure:
- Acute Kidney Failure: This occurs suddenly, often due to an injury, infection, or blockage. It can be reversible with prompt treatment.
- Chronic Kidney Failure: This develops gradually over time, usually as a result of long-term conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. It is often irreversible and may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
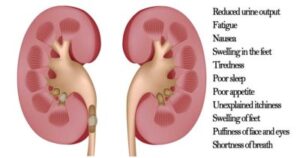
Symptoms of kidney failure can include fatigue, swelling in the legs and feet, shortness of breath, nausea, confusion, and reduced urine output. If left untreated, kidney failure can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, and even death.
Why Does Kidney Failure Occur?
Kidney failure can result from a variety of causes, some of which are preventable, while others are related to underlying health conditions. Here are the most common reasons:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys over time, leading to chronic kidney disease and eventual failure.
- High Blood Pressure: Uncontrolled hypertension can strain the blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to function.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Long-term damage to the kidneys from conditions like glomerulonephritis or polycystic kidney disease can progress to kidney failure.
- Acute Injuries: Sudden damage to the kidneys from severe dehydration, infections, or trauma can cause acute kidney failure.
- Blockages: Conditions like kidney stones, tumors, or an enlarged prostate can obstruct urine flow, leading to kidney damage.
- Medications and Toxins: Certain medications (e.g., NSAIDs) and exposure to toxins can harm the kidneys.
- Other Health Conditions: Autoimmune diseases, heart failure, and liver disease can also contribute to kidney failure.
Prevention of Kidney Failure
While some risk factors for kidney failure, such as genetics or aging, cannot be changed, many causes are preventable. Here are some practical steps to reduce your risk of kidney failure:
- Manage Diabetes and High Blood Pressure: These are the leading causes of kidney failure. Work with your healthcare provider to keep your blood sugar and blood pressure levels under control through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps the kidneys flush out toxins and prevents the formation of kidney stones. Aim for 6–8 glasses of water daily, unless advised otherwise by your doctor.
- Adopt a Kidney-Friendly Diet: A diet low in salt, processed foods, and animal protein can reduce strain on the kidneys. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. If you have kidney disease, consult a dietitian for a personalized plan.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, control blood pressure, and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Avoid Overuse of Medications: Certain medications, such as NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen), can harm the kidneys if used excessively. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and avoid self-medicating.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the kidneys, while excessive alcohol can dehydrate and strain them. Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake to moderate levels.
- Monitor Kidney Health: If you have risk factors for kidney disease, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, get regular check-ups to monitor your kidney function. Early detection can prevent progression to kidney failure.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit exposure to harmful substances like pesticides, heavy metals, and certain chemicals, which can damage the kidneys.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of diabetes and high blood pressure, both of which can lead to kidney failure. Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Treat Infections Promptly: Untreated infections, especially urinary tract infections (UTIs), can spread to the kidneys and cause damage. Seek medical attention if you suspect an infection.
The Importance of Early Detection
Kidney failure often develops silently, with no noticeable symptoms in the early stages. Regular screenings, especially for those with risk factors, are crucial for early detection. Simple tests like blood tests (to measure creatinine levels) and urine tests (to check for protein) can assess kidney function. Early intervention can slow or even prevent the progression of kidney disease.
Conclusion
Kidney failure is a serious condition, but understanding its causes and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk. By managing chronic conditions, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and staying vigilant about your kidney health, you can protect these vital organs and maintain overall well-being.
Contact
32/1, North Mugda, P.O : Basabo, P.S : Mugda, Dhaka-1214, Bangladesh
Mobile: +8801712-651032
Copyright © 2025 Hello Charity | Powered by SoftWeb IT