Diabetes
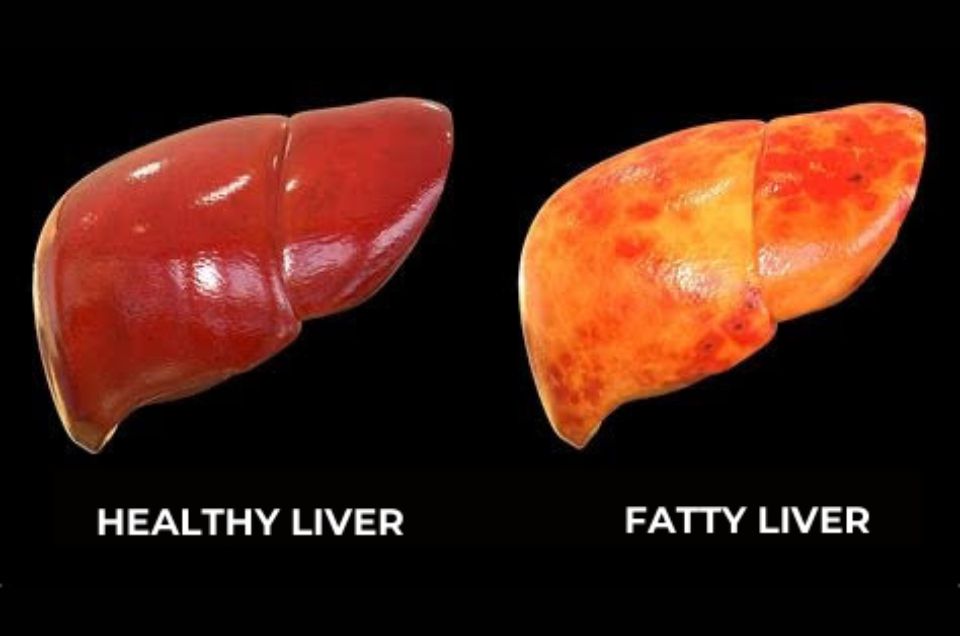
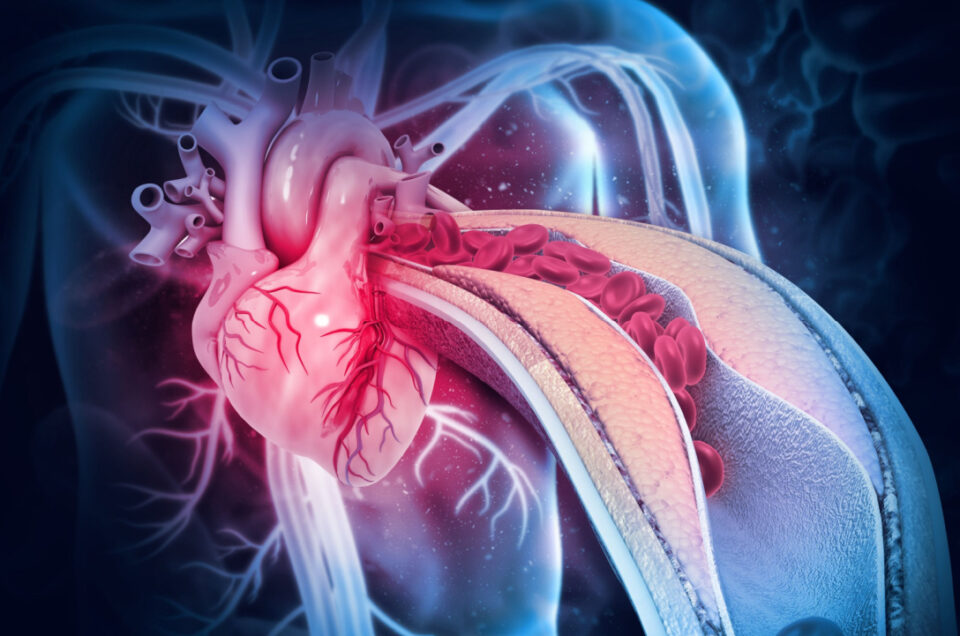
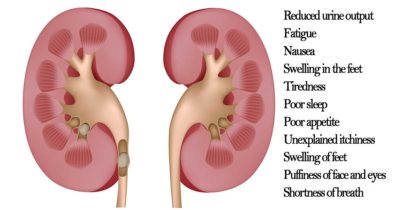
+880171234556 chairman@eshoi.org Follow Us: Home Services Programs Doner About Chairman Massage Our Team Blog Contact Home Services Programs Doner About Chairman Massage Our Team Blog Contact Become a Member What is Diabetes? | Why Does Diabetes Occur? | Prevention of Diabetes. eshoiorg March 5, 2025 What is Diabetes? Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period. This happens when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It usually develops in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy. Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. It is often linked to lifestyle factors and can develop at any age. Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes cause insulin resistance. It usually resolves after childbirth but increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes later in life. Symptoms of diabetes can include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss. Why Does Diabetes Occur? The causes of diabetes vary depending on the type, but they often involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Here’s a closer look at why diabetes occurs: Type 1 Diabetes: The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to result from an autoimmune reaction triggered by genetic predisposition and environmental factors, such as viral infections. Type 2 Diabetes: This form is strongly linked to lifestyle factors, including poor diet, physical inactivity, and obesity. Genetics also play a role, as a family history of diabetes increases the risk. Gestational Diabetes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause insulin resistance. Women who are overweight, have a family history of diabetes, or are older during pregnancy are at higher risk. Other risk factors for diabetes include: Age: The risk of Type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45. Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and South Asians, are more prone to diabetes. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS have a higher risk of developing insulin resistance and diabetes. Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance. Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of diabetes. Prevention of Diabetes While Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, Type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes are largely preventable through lifestyle changes. Here are some practical steps to reduce your risk: Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Losing even a small amount of weight (5–10% of body weight) can significantly reduce your risk. Adopt a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, refined carbs, and saturated fats. Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps your body use insulin more effectively and lowers blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: If you have prediabetes (higher-than-normal blood sugar levels), regular monitoring can help you take action before it progresses to diabetes. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking increases insulin resistance, while excessive alcohol can lead to weight gain and blood sugar spikes. Quit smoking and drink alcohol in moderation. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to manage stress effectively. Get Regular Check-ups: If you have risk factors for diabetes, such as a family history or obesity, regular screenings can help detect early signs and allow for timely intervention. Stay Hydrated: Drinking water instead of sugary beverages can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes. Sleep Well: Poor sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate blood sugar. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night. Breastfeed Your Baby: If you’ve had gestational diabetes, breastfeeding can lower your child’s risk of developing diabetes and help you maintain a healthy weight. The Importance of Early Detection Diabetes often develops gradually, and many people don’t realize they have it until symptoms become severe. Early detection through regular screenings is crucial, especially if you have risk factors. Tests like fasting blood sugar, HbA1c, and oral glucose tolerance tests can help diagnose diabetes or prediabetes. Early intervention can prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes and its complications. Conclusion Diabetes is a serious condition, but understanding its causes and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and staying vigilant about your health, you can protect yourself from this chronic disease. About Contact About Contact Contact 32/1, North Mugda, P.O : Basabo, P.S : Mugda, Dhaka-1214, Bangladesh Mobile: +8801712-651032 Subscribe Us: Subscribe You have been successfully Subscribed! Ops! Something went wrong, please try again. Copyright © 2025 Hello Charity | Powered by SoftWeb IT
Read More »